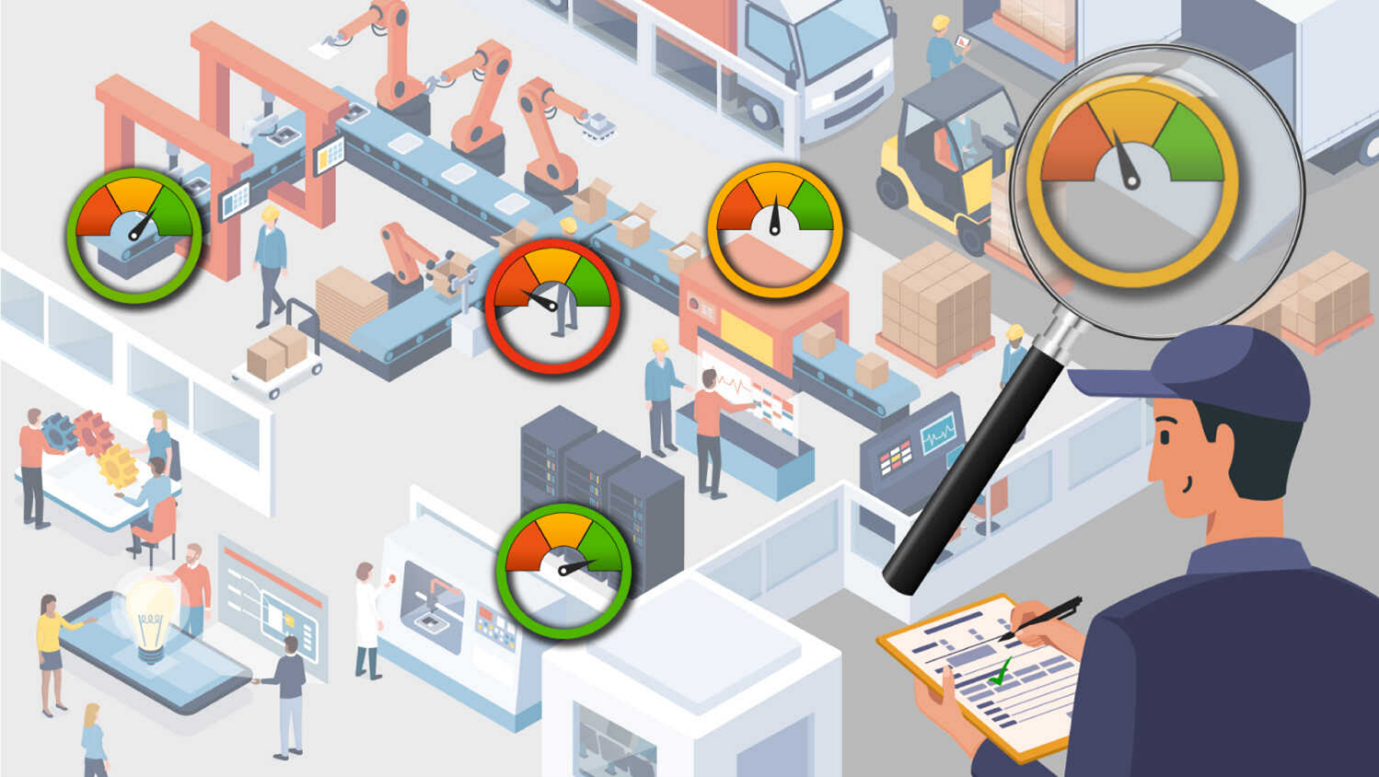
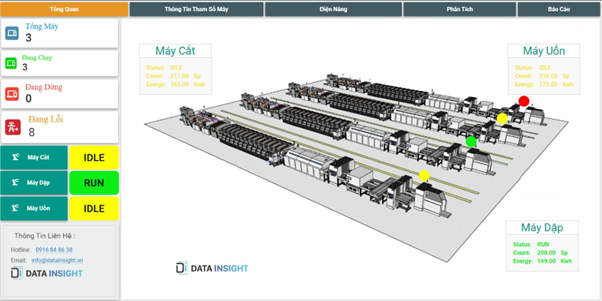
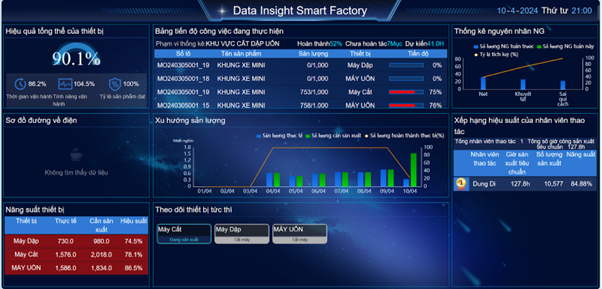
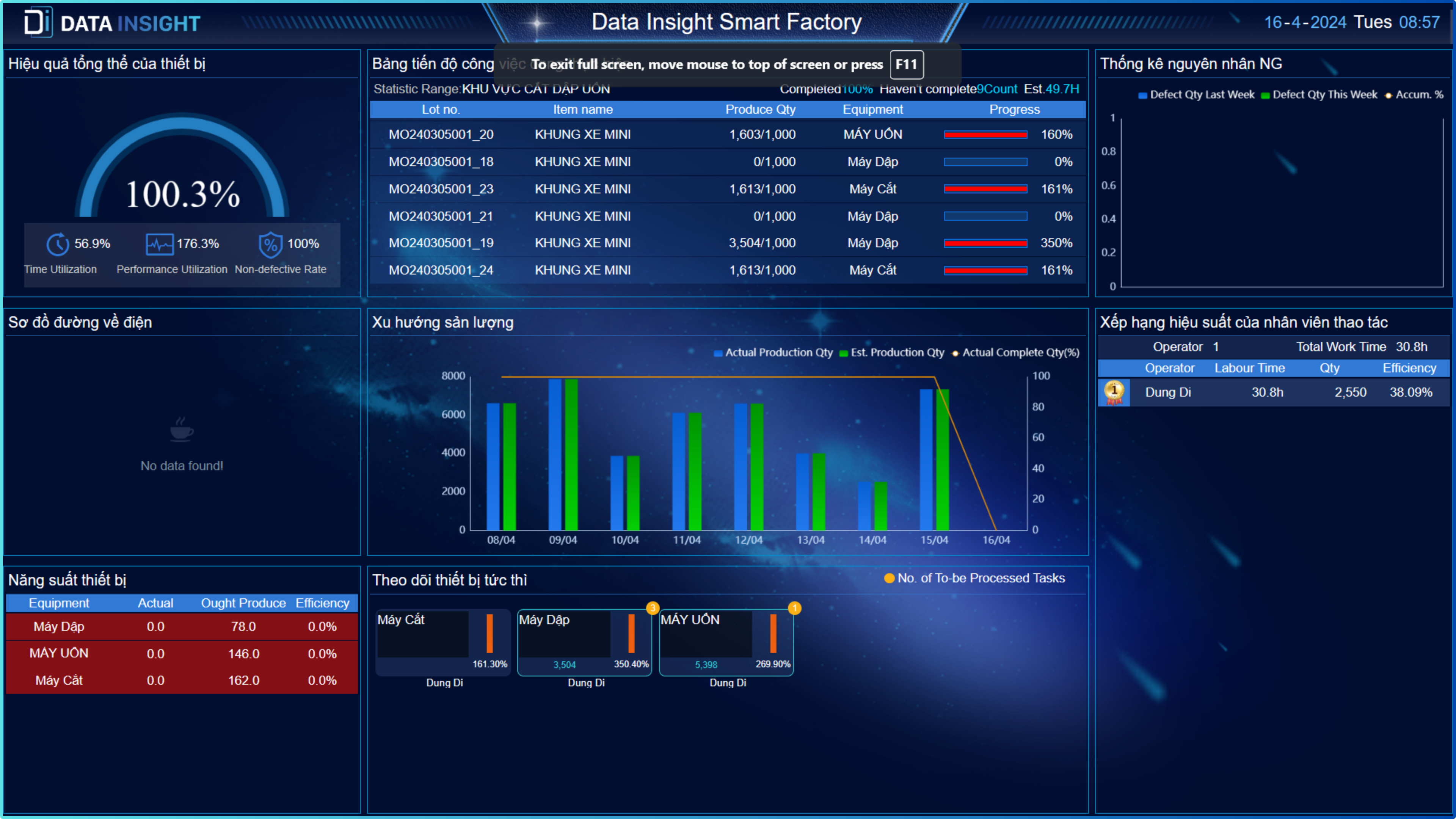
Most companies value the ability to enhance production plans. And the optimal for manufacturers is not investing in additional equipment while production capacity and productivity still increases. After all, the essence of manufacturing is producing goods, and modern operations are increasingly efficient in doing so.
In this article, we will explore exactly what production capacity is and the strategies that manufacturing businesses can use to uncover hidden capacity in their production scale.
What is Production Capacity?
Production capacity is the maximum output achievable in the process of manufacturing goods. It is a component-based metric, determining the maximum quantity of goods that can be produced based on a certain amount of resources (time, labor, materials).
For example: In a week, we can produce 500 units.
The ideal for any manufacturer is to operate at the best capacity of the equipment. This means all equipment is utilized at the highest rate and operates with optimized processes to avoid unnecessary downtime. However, capacity in most manufacturing companies is limited by one or a few factors.
Before we can work to increase production capacity, it is best to identify why our equipment is constrained by what bottlenecks.
To help you better understand the concepts and formulas related to calculating productivity and efficiency of the plant, we will clarify each concept mentioned below together.
The Six Big Losses
The Six Big Losses is a concept developed from Japan in the early 70s, representing types of losses that can limit the production capacity of a machine. These losses include:
Availability Losses (Equipment operation time):
- Equipment Failures: Including breakdowns and mechanical failures.
- Setup and Adjustment: Involving changeovers and machine adjustments.
Performance Losses:
- Idling and Minor Stops: Including small breakdowns and interruptions.
- Speed Reduction: Caused by poor maintenance or inexperienced staff.
Quality Losses:
- Process Defects: Resulting from human error and poor work processes.
- Yield Reduction: Including faulty parts and waste.
Productivity Calculation Formula
- Machine-Hour Capacity: This is a simple calculation of the number of machines multiplied by the number of hours available to run. This can range from single-day shifts to continuous operations.
- Output Capacity of One Product: Here, the time required to produce one unit is divided by the machine-hour capacity.
Manufacturing Potential of Multiple Products: Most factories produce more than one product. In this case, each product is calculated as it would be for a single product, then added to the output of the other product. If the time to produce each item is different, then the combination of units per hour up to the maximum capacity is determined by order position, or schedule, to work within that capacity.
Once the capacity is known for all equipment, the impact of the Six Big Losses will result in a utilization level for each machine and the factory. Increasing capacity means understanding and managing those variables favorably. This is done by combining metrics that help define the utilization rate and the gap required to address it and improve.
1. Machine-Hour Capacity (MHC):
MHC = Number of machines that can be used x Hours available to operate.
2. Output Capacity of One Product:
Production capacity = MHC / Hours to produce one product.
3. After calculating the capacity of each product, you can calculate the total output rate of the factory for multiple products:
Capacity for multiple products = (Number of product 1 x hours to produce product) + (Number of product 2 x hours to produce product)
Once the formulas indicate the requirements for overall capacity for each product, the capacity of the factory can be determined through multiple iterations. They include:
- Total factory capacity
- Monthly, weekly, or daily production yield
- Capacity per machine
Why Increase Production Capacity?
Companies seek ways to increase capacity for various reasons. This may be to meet actual increases in demand or planned increases in demand. They may also be used for short-term and long-term spikes in demand as well. Regardless, several basic strategies help companies develop a production capacity calculator to increase production capacity and optimize a manufacturing plant to take on the extra load.
Short Term
Use Current Equipment: Using current equipment, more may result in overtime, including weekends or nights. It may also mean adding shifts in manufacturing plants that don’t have a continuous operation.
Outsource: This essentially uses someone else’s equipment to manufacture a part or all of a product. However, this may cost manufacturers a premium.
Long Term
Optimize Equipment Utilization: This means deploying tools and methods to improve the performance of existing equipment to “unlock” hidden capacity.
Purchase Additional Equipment: Ideally, purchasing new equipment is considered when existing equipment is optimized and at its maximum capacity. If this is the case, justifying such a significant capital expense will be far easier.
Metrics for Increasing Manufacturing Capacity
Short-term increases run the risk of being expensive and even dangerous. If the run lasts longer than planned, overtime becomes a drag. And by outsourcing, there is always a chance of competitors attempting to copy your product. But long-term increases can be achieved that lowers cost and protects companies from the risk of duplication.
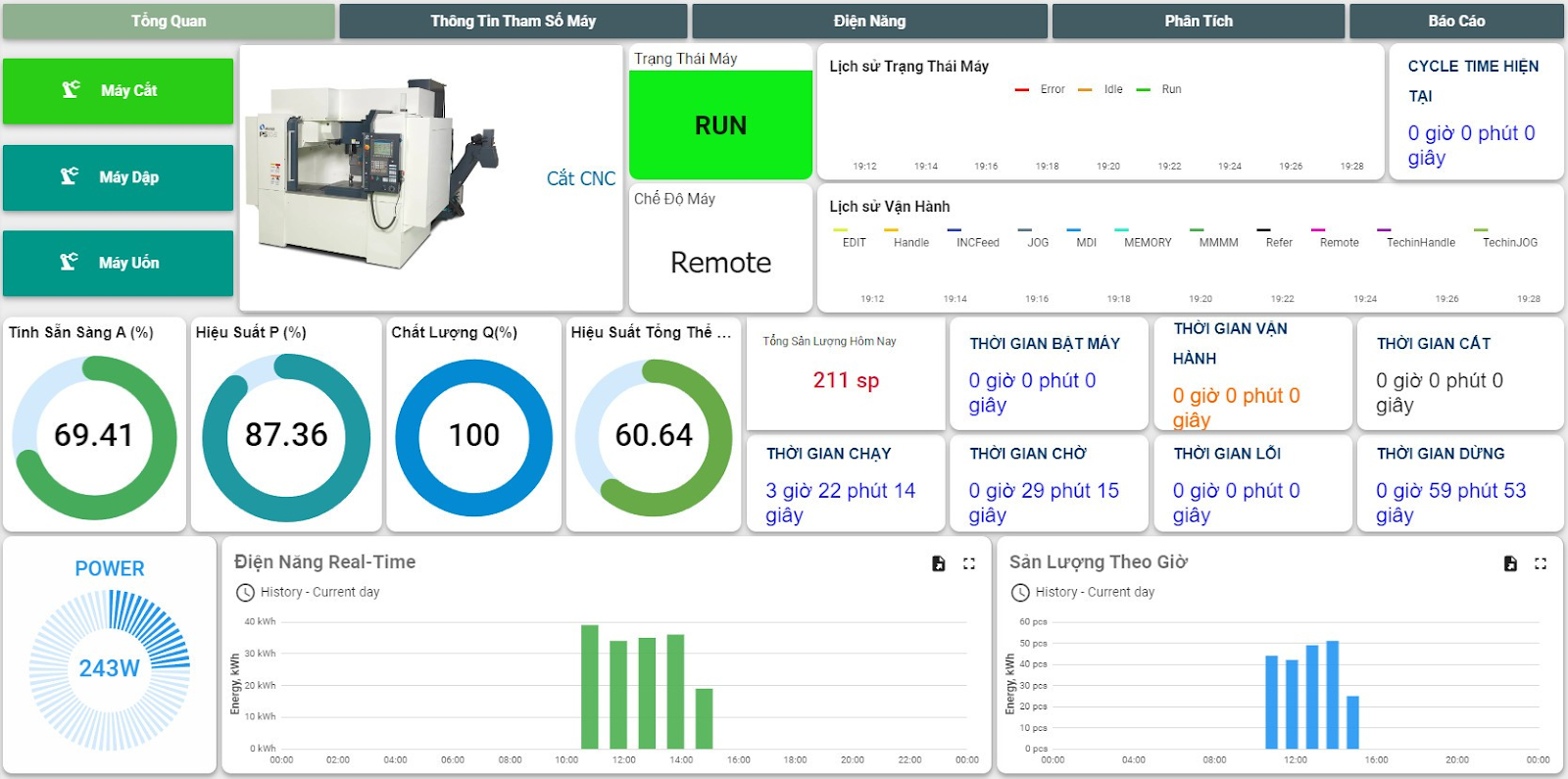
The key to unlocking hidden capacity is using best-in-class manufacturing production software and devices designed to capture, analyze, and contextualize data so that leaders can better understand and improve their operations’ performance. By benchmarking progress, manufacturers can automate their production capacity calculator and processes to begin to fully optimize their equipment utilization and uncover paths for improvement.
5 Steps to Increase Production Capacity
Increasing productivity to meet customer demand is a complex process. Here are some ways to achieve this:
1. Reduce Machine Downtime
Machine downtime affects everything a manufacturing plant produces, including raw material management, labor, scheduling, etc. Reducing machine downtime frees up the overall capacity of the plant to better meet service level requirements.
Machine downtime should be categorized as part of a process improvement strategy. These improvements will reduce downtime, improve line efficiency, increase the number of production units per hour, and increase the overall capacity of the plant.
2. Increase Employee Work Hours
The most common approach for an immediate or short-term increase in the overall capacity of a plant is overtime. This strategy may be feasible in seasonal manufacturing or during uncertain times. However, over time, it can become costly.
An alternative is to add an additional straight-time working shift, assuming the current operation is not a continuous 24/7 facility. Here, an estimate of future financial performance may indicate that the required shifts will be sustained over time with new demand.
However, extending overtime and additional shifts assumes that the average efficiency of the plant is optimized and that the manufacturing process has already undergone improvements to maximize actual output per hour. Extending hours or shifts with inefficient processes is costly and does not increase machine productivity.
3. Evaluate Supplier Capacity
Most companies in the manufacturing industry tend to focus on internal capacity when considering productivity, but supplier capacity can also impact yours. Supplier quality issues can reduce your productivity by decreasing the number of first-quality production units and requiring more inspection.
Shipment of incorrect parts or raw materials will have a similar impact. Late shipments will idle your equipment until expedited measures are taken to receive goods. Evaluating suppliers can have a significant impact on your productivity.
4. Improve Internal Processes
Similar to reducing machine downtime, improving internal processes will increase production speed and optimize labor usage. Two traditional process improvement methods are Lean and Six Sigma.
These are still good improvement strategies but are best implemented using a machine data platform. Real-time data and analytics can enhance Lean improvement strategies, unlocking hidden productivity for the entire production process.
5. Use a Machine Data Platform
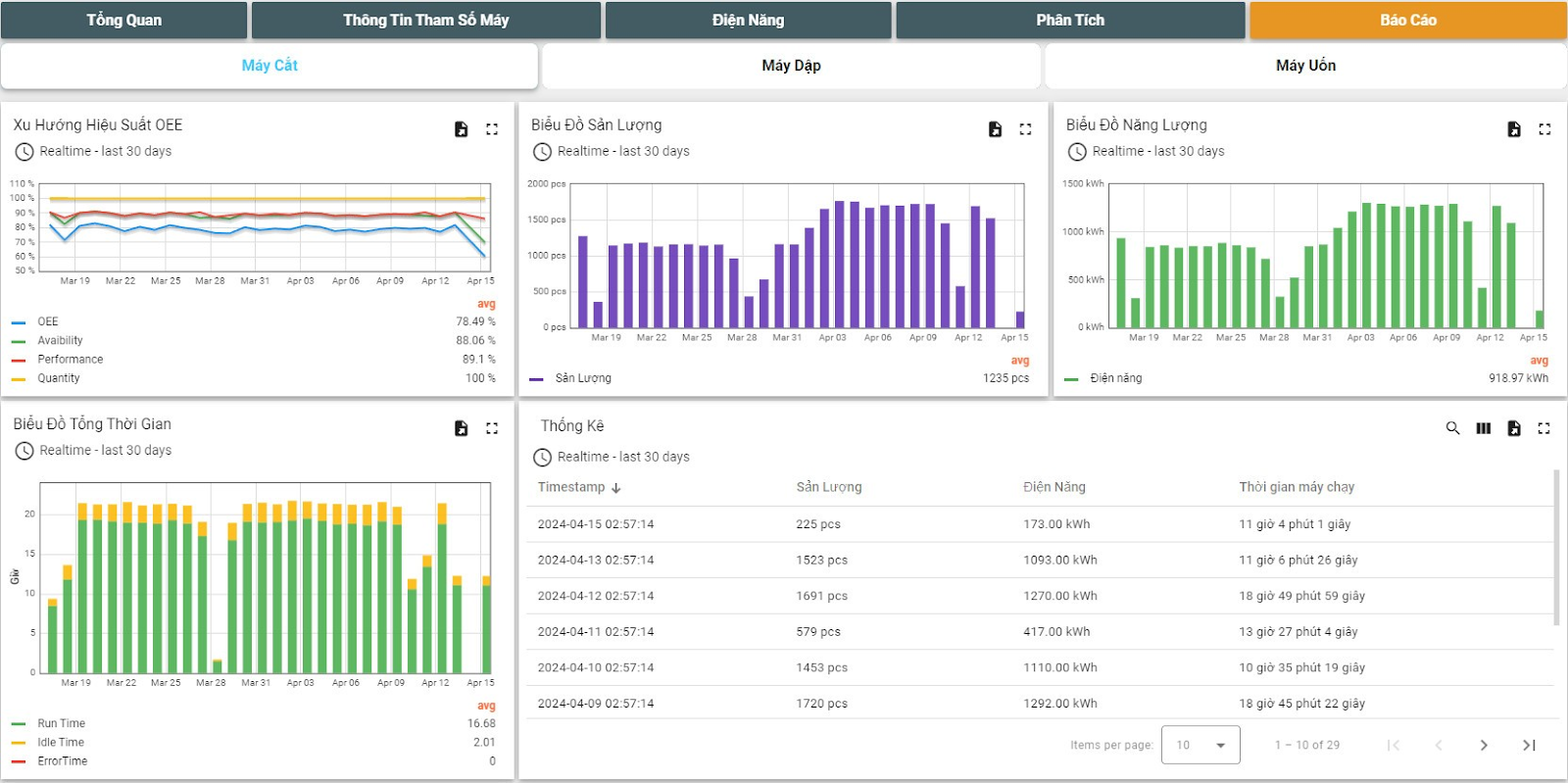
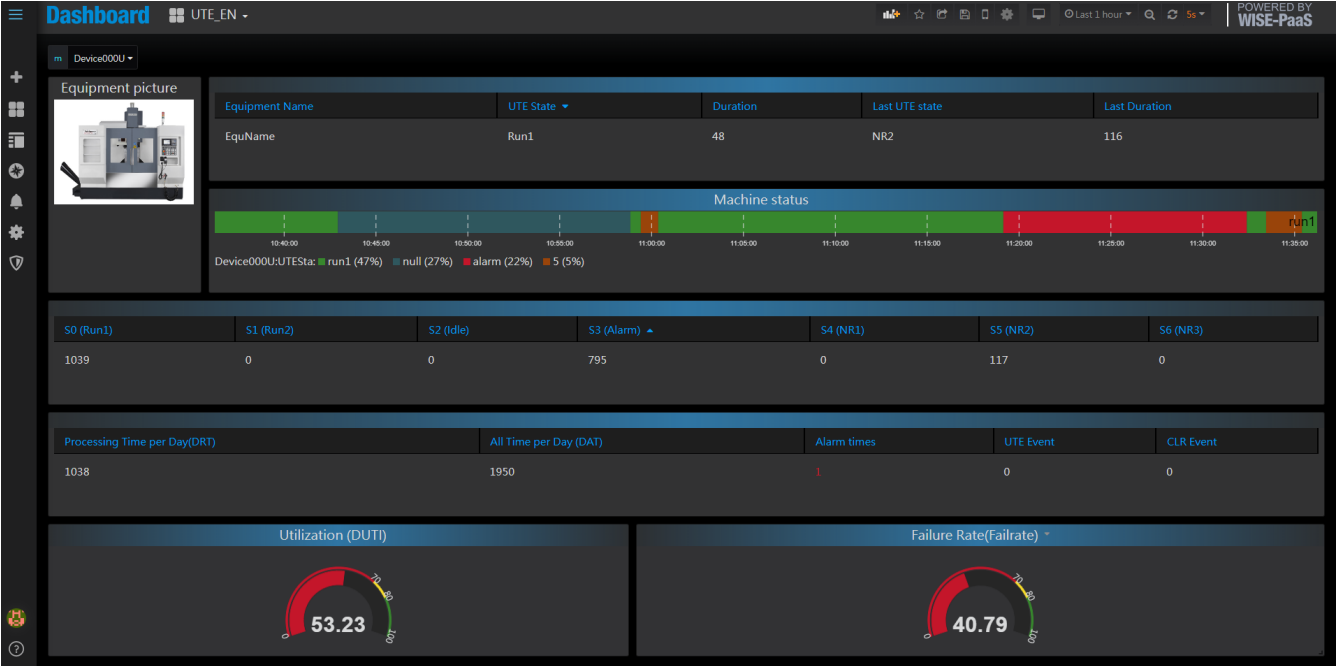
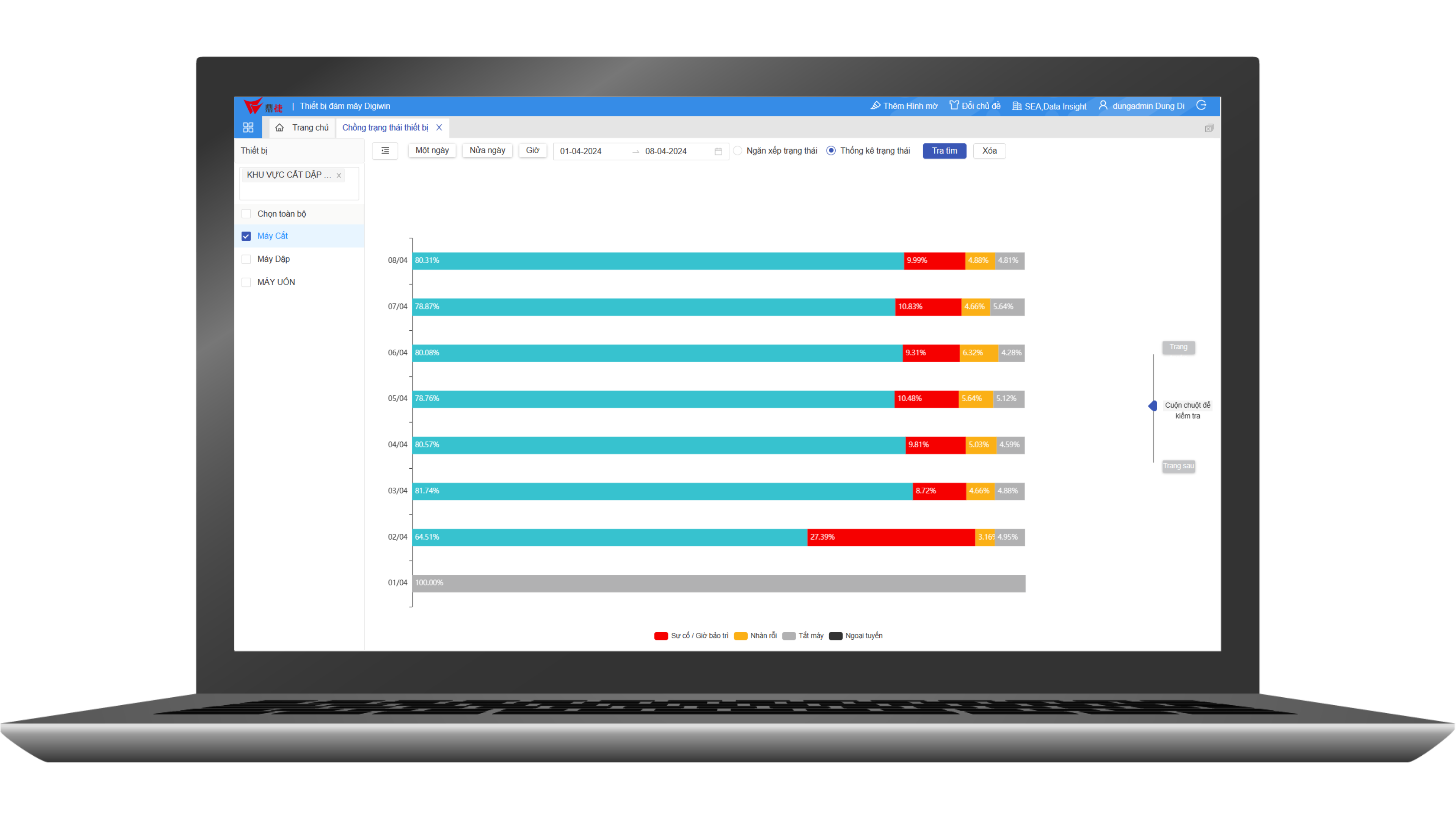
The best way to increase productivity is to use a machine data platform. All the steps above can be consolidated into a single platform based on real-time data and advanced cloud-based analytics. The results are dynamic, and the success of improvements can be measured immediately. Productivity can be continuously measured to unlock machine productivity across the entire factory floor.
A machine data platform provided by Data Insight will use digital technology to calculate productivity, plant performance for you. With real-time machine data and accurate analytics.
Interested? Contact us now at!
DATA INSIGHT TECHNOLOGY VIETNAM COMPANY LIMITED
- Hotline: 0916.848.638
- Hanoi office: Số 6 Kim Đồng, phường Giáp Bát, Quận Hoàng Mai, Thành phố Hà Nội, Việt Nam
- HCM City office: 99 đường Cộng Hòa, Phường 4, Tân Bình, Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh, Việt Nam